Applications
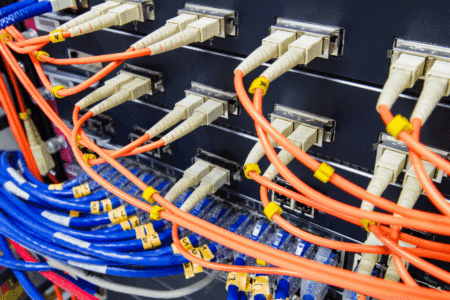
As the popularity of optical fibers continue to grow, so does their applications and practical uses. Fiber optic cables became more and more popular in a variety of industries and applications.
- Communications / Data Storage
- Mechanical or Industrial
- Networking
- Internet and telecommunications
- Automotive Industry
Fiber optics are the best choice for businesses requiring long distance cabling and high bandwidths, as it’s reliable and can support future growth.
Few more Advantages are:
- fiber-optics are replacing copper wire as an appropriate means of communication signal transmission
- Support of higher bandwidth capacities.
- Light can travel further without needing as much of a signal boost.
- They are less susceptible to interference, such as electromagnetic interference.
- They can be submerged in water- fiber optics are used in more at-risk environments like undersea cables.
- They do not need to be maintained or replaced as frequently.